Decision Tree
Decision Trees are a way to represent comparison-based algorithm Comparison-Based Algorithm. Where each leaf represent a permutation (a possible answer) and each node is a comparison.
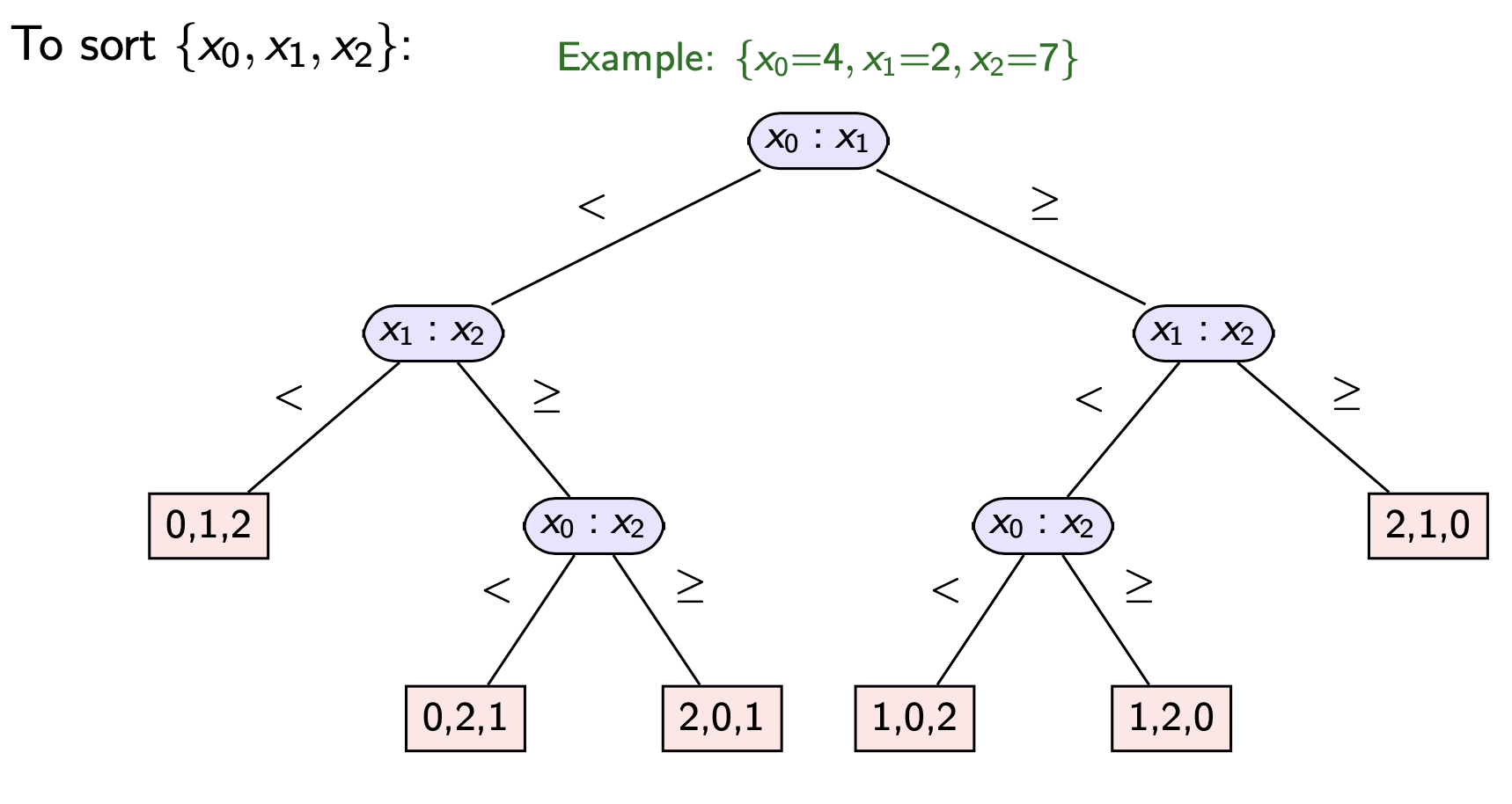 So in the example array [4, 2, 7] will arrive at leaf [1, 0, 2] after 3 comparisons according to the tree.
So in the example array [4, 2, 7] will arrive at leaf [1, 0, 2] after 3 comparisons according to the tree.
Thoughts:
- Use it for comparison-based algorithms and when they ask about the worst case number of comparisons like they did on the midterm.
- First, find the number of leaves, that is the number of possibilities/answers we have, and secondly find the height of the tree. Usually : two results for comparisons or : three results for comparisons.
- Then set # leafs height of tree, solve for (in # leafs).